Bones in the Human Body – Spine and Ribcage
Video Lesson Description
In this video lesson, you will discover such Bones in the Human Body as the vertebral column and the thorax or ribcage.
Bones in the Human Body – the vertebral column and the thorax
Let’s begin with the Bones in the Human Body – Spine.
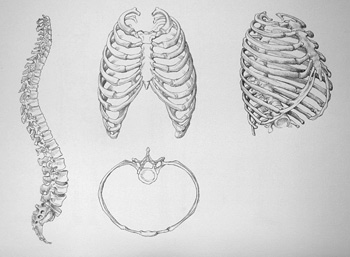
The vertebral column or spine is a flexible structure that bears the weight of the human body. It is made up of a series of vertebrae, which can be divided into five regions as follows:
– The cervical region – which consists of the seven upper vertebrae
– The thoracic region comprises 12 vertebrae
– The lumbar region with 5 vertebrae
– The sacral region (or sacrum) – which contains 5 fused together vertebrae
– The coccygeal region – which contains 4 to 5 vertebrae
With the exception of the first and second vertebrae, each separate vertebrae of the spine is separated from others by the intervertebral discs, which allow various movements of the spine and absorbs the shockwaves during walking, jumping and running.
Vertebrae have a hollow interior, through which the spinal cord goes.
In the spine’s normal position, only the 7th cervical vertebra and the 1st thoracic vertebra are noticeable on the back. Other spinous processes become noticeable as Bones in the Human Body only during the flexion of the spine when the model bends forward.
The average male spine is longer than the female’s. The vertebral column measures around 28 inches, which is about 40 per cent of the total body height.
To amortize the body weight and the weight of bones in the human body, the spine is elegantly waved and curved. This fact is very important as it helps fine artists to depict the natural flow of the vertebral column, which influences the shape of the back. There are four curves of the vertebral column as follows:
– Cervical curve
– Thoracic curve
– Lumbar curve
– Sacral curve
Apart from providing a strong support for the cranium and torso, the vertebral column is also flexible enough to provide various movements to the body and other bones in the human body.
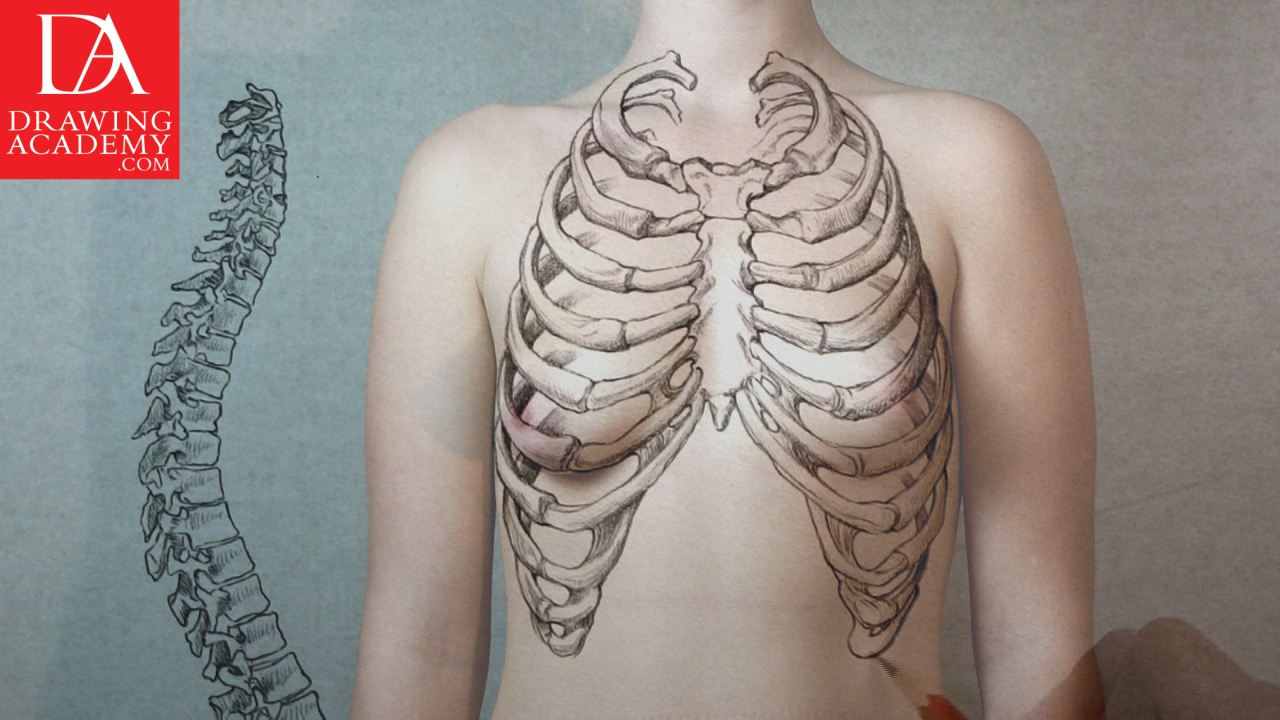
Now, let’s examine the thorax or ribcage, which is integral part of bones in the human body. It contains and protects the internal organs – the ones which deal with respiration and circulation. The ribcage structure is made up of bones and cartilage. There are 12 pairs of ribs, on either side of the thorax, which gives 24 bones in total.
Ribs are connected on the back to the 12 thoracic vertebrae. In front of bones in the human body, the first 7 pairs are joined with the sternum (or breastbone) and therefore, known as true ribs. The lower five pairs of ribs are called false ribs, the last two of which are called floating ribs.
The costal cartilage, forms the skeletal or anatomical arch of the bones in the human body. It has a pointed angle and is clearly visible on people with less fat and muscles under the skin.
People with more developed abdominal muscles tend to have a differently shaped arch, which is called the abdominal arch and marked by a yellow line here. This arch is also known as the Greek arch, because classical canons of ancient Greek and Roman art were focusing on the ideal human body with well developed muscles; sculptors often emphasised this arch. The Greek arch is formed by the muscular bulge of the upper section of the rectus abdominis muscles, which we will examine in the video lesson dedicated to the torso muscles and bones in the human body.
The sternum or breastbone is located in front of the chest and ribs and connected to this bone via cartilage. The breastbone has three portions:
– The manubrium is the top section where the medial ends of the clavicle bones are attached (not showed here) and the first pair of ribs joins to this bone via cartilage
– The gladiolus or body of sternum where the 2nd to 7th pairs of ribs are attached
– The xiphoid process
All 12 pairs of ribs are entirely suspended from the vertebral column. As the spine and other bones in the human body move or rotate, it causes the ribcage to slightly change its shape as well, so it is not a rigid structure. Ribs are in constant movement when a person is breathing.
Generally, males and females have 12 pairs of ribs. However, the number of ribs is not constant for everyone. Some people have 13 pairs or less than 12. Others may have an odd number of ribs as opposed to pairs.
The ribcage has quite a rounded shape comparing to other bones in the human body. The rib connects to the spine by the head of the rib; the rib also connects to the transverse process of vertebra. The spinous process is pointing backward.
Others parts of the vertebra are:
– The laminae
– The vertebral arch
– The pedicle
– The ventral body
All ribs are narrow and flattened. They have a downward sweep from the spine. This downward angle of ribs increases from the horizontal level the lower the ribs are. The neck ribs are narrow. From the top to the base, the ribcage gradually becomes wider, because each next rib has a greater radius of curvature than the rib above it.
The breastbone or sternum has the sternal angle. The angle of the manubrium is slightly different than the angle of the gladiolus.