Muscles of a Foot – Anatomy for Fine Artists
In this video lesson you will discover the major Muscles of a Foot every figurative fine artist must know to draw a foot realistically.
Enroll in the Drawing Academy Course
Pay once - Enjoy forever!
Only $297
Muscles of a Foot
Muscles of the foot can be divided into intrinsic and extrinsic muscles.
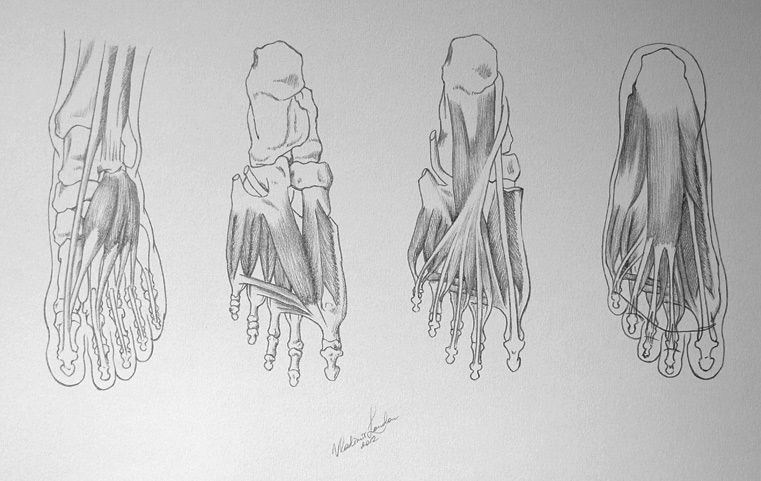
Intrinsic muscles are short and attach to the foot bones, while long extrinsic muscles originate outside of the foot, on the bones of the lower leg – the fibula and the tibia.
Intrinsic muscles are arranged in four layers, three of which are located on the sole of the foot (or plantar region). These layers are difficult to detect as they are covered by fatty tissue and fascia. The first layer of intrinsic muscles is the most visible.
We begin with the extensor digitorum brevis, which is located on the dorsal side of the foot. It originates on the upper and lateral surface of the calcaneus and inferior extensor retinaculum. This muscle inserts into the 1st to the 4th phalanges of the toes. Some sources consider the first part of this muscle as a separate muscle, called the extensor hallucis brevis, which inserts into the great toe’s phalanx.
The extensor digitorum brevis helps straighten or extend bent toes, while the extensor hallucis brevis extends the great toe.
Here is the plantar view of the deep layer of the left foot. Here we can see:
– Tendon of peroneus longus
– Interossei muscles
– Flexor hallucis brevis
– Adductor hallucis (oblique head)
– Adductor hallucis (transverse head)
The adductor hallucis has two heads—oblique and transverse. This muscle is responsible for adducting the big toe. The oblique head of this muscle is a large, thick, fleshy mass crossing the foot obliquely and occupying the hollow space under the first, second, third and fourth metatarsal bones. The transverse head is a narrow, flat fasciculus which arises from the plantar metatarsophalangeal ligaments of the third, fourth, and fifth toes (sometimes only from the third and fourth), and from the transverse ligament of the metatarsus. It is inserted into the lateral side of the base of the first phalanx of the great toe, its fibers blending with the tendon of insertion of the oblique head.
The flexor hallucis brevis arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the cuboid bone, from the contiguous portion of the third cuneiform, and from the prolongation of the tendon of the tibialis posterior – which is attached to that bone. It divides in front into two portions, which are inserted into the medial and lateral sides of the base of the first phalanx of the great toe – a sesamoid bone being present in each tendon at its insertion.
Here is the middle layer of the foot’s plantar region.
On this drawing you can see:
– Tendon of flexor hallucis longus
– Tendon of peroneus longus
– Quadratus plantae
– Insertion of peroneus brevis
– Flexor digitorum longus
– Flexor digiti minimi brevis
– Lumbricales
The lumbricals are four small skeletal muscles, accessories to the tendons of the flexor digitorum longus. The muscles end in tendons, which pass forward on the medial sides of the four lesser toes, and are inserted into the expansions of the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus on the dorsal surfaces of the proximal phalanges. All four lumbricals insert into the extensor hoods of the phalanges, thus creating an extension at the inter-phalangeal joints. As the tendons also pass inferior to the metatarsal phalangeal joints, it creates flexion at this joint.
This is the drawing of the superficial layer of the plantar region of the left foot.
You can see here:
– Abductor digiti minimi
– Abductor hallucis
– Flexor digitorum brevis
– Flexor digiti minimi brevis
– Flexor hallucis longus
Let’s have a closer look at some of those muscles.
The abductor digiti minimi is located on the outer margin of the foot. It originates on the calcaneal tuberosity and the lateral process of the calcaneus, the plantar aponeurosis and the fifth metatarsal bone. This muscle inserts into the base of the proximal phalanx of the little toe. The abductor digiti minimi abducts the little toe and also helps to flex it.
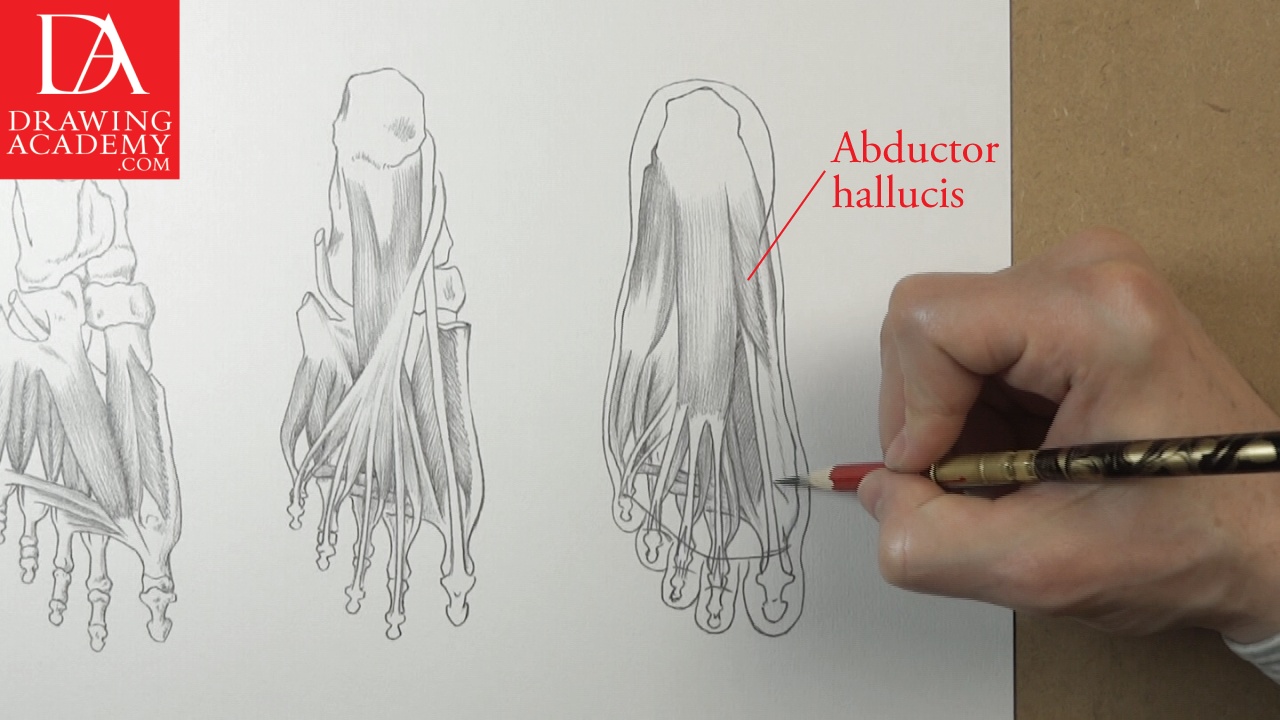
The abductor hallucis forms the inside margin of the foot. It originates from the medial process and the calcaneal tuberosity of the calcaneus and the plantar aponeurosis.
This muscle inserts into the base of the proximal phalanx of the great toe.
The abductor hallucis helps in abducting the great toe.
The flexor digitorum brevis is the most superficial of all the plantar muscles. It begins from the calcaneal tuberosity and the medial and plantar surface of the calcaneus and inserts into the middle phalanges of the lesser toes on the plantar surface. This muscle flexes the four toes at the proximal inter-phalangeal joints.